Overall Introduction of Light Stabilizers
What Is Light Stabilizers (HALS)? definition of light stabilizer
One main category of light stabilizers consists of what are known as Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers (abbreviated as HALS). They are derivatives of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine and are extremely efficient stabilizers against light-induced degradation of most polymers.
HALS which are efficient scavengers and function by inhibiting degradation of polymers that have already formed free radicals, they do not absorb UV radiation but act to inhibit degradation of the polymer. They slow down the photochemically initiated degradation reactions, to some extent in a similar way to antioxidants. Mechanism different of antioxidant and HALS is HALS reaction is cyclic while antioxidant is not.
Commercially, Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers are now the single most important light stabilizers, followed by benzophenones and benzotriazoles.
Synonyms of Light Stabilizer
- Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers (abbreviated as HALS)
- light stabilizer additive
- ultraviolet light absorber
How Does Light Stabilizers Work? the mechanism of light stabilizers
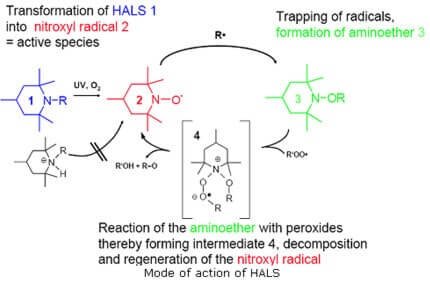
The mechanism is not fully understood. Hydroperoxide decomposition and free radical scavenging certainly play a part, as also does the regeneration of HALSs, where UV absorbers are frequently consumed as a result of their operation. There are several theories for how this works – possibly by energy transfer, free radical termination(as photo below), or peroxide decomposition. Significant stabilization is achieved at relatively low concentrations and it appears that the HALS is actually regenerated by the stabilization process, rather than consumed by it. Theory suggests that the hindered amine oxidizes to form amine-ether, which is a non-radical species.
The effectiveness of HALS systems does not depend on the thickness of the plastics product and they are therefore particularly useful for the protection of surface layers and in thin sections. Agents are of low or high molecular weight. Polymeric HALSs offer superior compatibility, low volatility, excellent resistance to extraction, and contribute to heat stability. Combination of two high molecular weight grades gives a good balance of properties in the greenhouse film, which is the main use of HALSs in LDPE film.
Synergistic Effect of Light Stabilizers And UV Absorber
UV absorbers are not able to absorb all of the UV radiation that product is exposed to. Some UV radiation will penetrate the surface. Because of this, HALS are incorporated into the polymers. These molecules work by scavenging any free radicals that do form – this is different from UV absorbers, which prevent their formation in the first place HALS function by removing radicals from the system and subsequently regenerating themselves. Most formulators will use a combination of absorbers and HALS for this reason.
Synergistic combinations of UV absorbers and HALS are optimal for the stabilization of polymer. UV absorbers are governed by the Beer-Lambert Law
thus absorbance is linearly related to the concentration of UVA (320 to 400 nanometers (used for photocuring), its molar absorptivity (extinction coefficient), and path length (coating thickness). HALS are free radical scavengers and are not subject to Beer’s Law and work anywhere in the system.
UV Absorber & Light Stabilizers Market And Trend
In the year 2015, global plastic and coating UV absorber (include light stabilizers) market scale is about 13 Billion RMB, and with 3% to 4% compound average growth rate(CAGR) in next four years. This attributes to industrial development in emerging market plus significant growth in demand for coating globally. For example, automotive and industrial paint has driven the demand for polymer additives. With the threshold of high techniques in additives manufacturing and developing, UV absorbers (include light stabilizers) manufacturers were located in few chemistry-developed countries. Opportunities for growth exist in the new market and exploring new applications.
How To Choose Light Stabilizers (HALS)?
General Rules to Follow When Choosing Antioxidant and UV Stabilizers
1. Stability & Extraction
Uv Stabilizers and antioxidant hydrolysis resistance are ok,it are the color stability needs to pay attention. Also, there two additives shall not react with other ingredients in the system, neither corrosion equipment nor extract by the substance on article surface.
Hindered amine light stabilizer normally shows low alkalinity, no acidic additives shall be used together, and final article shall not apply to the acidic environment.
2. Solubility & Compatibility
Most polymers are non-polar while antioxidant, UV stabilizer are somewhat polar. Solubility is an issue need to concern. Antioxidant and UV stabilizers shall dissolve while not decompose in polymers processing temperature which most UV stabilizer could meet this requirement.
3. Migration
When possible, high molecule weight and relatively high melting point antioxidants and UVA shall be selected, each dosage shall determine based on most stringent processing and end-user environment.
4. Processing
When antioxidant and UV stabilizer melting range quite differ from resins’. Bias current or stick to screwing could occur. When this gap exceeds 100 ℃, UV stabilizer and antioxidant shall add in masterbatch form then mix with resin to process.
5. Handling and Safety
Antioxidant and UV stabilizer shall non or low toxic. No or low dust. Not harmful to human during plastic process and lifetime. Not harmful to animal or plates. No pollution to air,earth and water.
For agriculture file, food packing, toys, disposable infusion set or direct food, drug, medical device, medical devices, human contact plastics. Only FDA or EU approval antioxidant and UV stabilizer follow maximum concentration is allowed.
Typical Use of Antioxidant, UV Absorber, Light Stabilizer For Plastics
The information below is not to be construed as a warranty or representation for which we assume legal responsibility, it would change without any statement, Users should undertake sufficient verification and testing to determine the suitability for their own particular purpose of any information or products referred to herein.if any questions when choosing these additives for your material,please contact our support team by (Click Here).
For Antioxidants (Click Here), jump to antioxidant product portfolio page.
For UV Absorber/Light Stabilizer (Click Here), jump to product portfolio page.
| Material | Application | Antioxidants | UV Absorber/HALS | Remark | |
| POLYOLEFIN
| PP thick section | 260-280℃ Outdoor table&chair | 1010+DSTDP | 622+326 | DSTDP=3*1010 |
| PP thin section Fiber & strip | 240-300℃ | PP fiber:1425
| Fiber: 770 without heat 622with heat Strip:791 | Low volatile Heat stability Extraction resistance Gas yellowing | |
| HDPE | 180-240℃ blowing, injection, extrusion | 1010+168 | 791,944 | Compatibility | |
| LDPE | Film, packing, cover, mulch, greenhouse cover | 1010 | 622+531 | <0.1% | |
| LLDPE | Film, blowing, injection | 1010+168 | 944/622+531 | / | |
| PEX | Wire cable | TMB 6 | / | / | |
| PB | Pipe | 1010+ DLTDP | Extraction resistance | ||
| STYRENICS | PS | Instrument&lamp shell | 1076 | UV P+770 | / |
| SAN | Kitchenware Electrical Automotive | 1076+168 | UV P+770 | / | |
| IPS | / | 245,1076 | UV P+770 | 0.1~0.25% | |
| HIPS | 245 | / | / | ||
| MBS | / | 1076+DLTDP | / | / | |
| ABS | Machinery industry / | 245+DLTDP | UV P+770 | High dosage Based on process technical | |
| SIS | Hotmelt adhesive pressure sensitive adhesion | 1076/1010 0.1-0.5% | UV P+770 Hotmelt adhesive 213 /770 pressure sensitive adhesion 213/770 | ||
| SBS | Sole,tar regulator | 1076/1010 0.1-0.5% | UV P | ||
| POLYURETHANE | PUR | Form,RIM,coating, adhesive, fiber
| 1076+5057 Aromatic amines<0.05%
| leather,elastomer,textile, sole, adhesive, fiber need UV absorber, | Color stain mechanical property gas yellowing |
| ENGINEERING | PC | Window | 1076+168 | UV P, 1577 | Color stain issue |
| POM | 220-230 | 245,1010 | 622+234 | Carbon black | |
| PET | Film,coating,bottle, Electricals,pipeline, conveyance | 1010 | 1577 | / | |
| PBT | 245 | 1577 | / | ||
| UPR | / | / | 329 | user to test and decide | |
| Aliphatic PA | Engine blade Heat sink cover etc. | 245/1098+168 | 944,770 | 0.2-0.7% | |
| TPEE | / | 329 | / | ||
| TPU | / | 1010 / 245+ DLTDP+445 | / | / | |
| PMMA | Glazing,signboard lamps | 0.05-0.2% UV P+770 Not always use together | / | ||
| PPE | / | / | UV P or 770 | ||
| PSU | / | / | / | exceed certain amount | |
| PVC | RPVC | / | / | UV P or 320 | |
| PPVC | / | 531+944 | |||
| ELASTOMER& | BR | 1520 | 320 | ||
| IR | 565 | 320 | |||
| SBR | Tire process, | 1520+TNPP | 320 | ||
| NBR | 1520+TNPP | ||||
| EPR,EPDM | Wire, roof film Liner, automotive | 1010 | 329+770 | ||
| Thermoplastic rubber | |||||
| TPO | 3052+168 | ||||
| X-SBR | Paper coating, carpet backing Nonwoven &textile liner | Cas 31851-03-3 Cas 26780-96-1 |
Selection Of Antioxidants For Use With UV Absorber
Care is needed in selecting anti-oxidants for use in combination with effective light-stabilization systems. High molecular weight stabilizers provide high levels of heat stability at normal application temperature. To avoid color shifts (especially yellow discoloration), BHT-free resins should be used with HALS formulations. Sulphur-containing organic compounds used as the-synergists are known to reduce the light stability level conferred by HALS, and high levels should be avoided.
| PE food contact | PE greenhouse film | PP coloured food contact | (General purpose | PP tapes, mouldings | PP coloured food contact | |
| Base resin | PH | PE | PP | PH | PP | PP |
| HMW-HAI.S | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low molecular weight | Yes |
| Benzophenone | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| food contact | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Thermal stabilization | good | good | Very good | Very good | Good | Limited |
| Application and let-down | Heavy-duty sticks: 1.5- 2.5%: film: 1.25-1.75%, 2.5-3.5%(24m); mouldings: 1.5-3% | Heavy-duty sacks: 1.5- 2.5%: greenhouse film: 1.25-1.75%. 2.5- 3.5 (24m) | Tapes: 1-3%; fibre: 1-3%: mouldings: 0.5-2.5% | Shrink wrap: 0.75-1.5%; greenhouse film:1-1.5%; HDPE crates: 0.25-0.5%; mouldings: 0.5-2.0% | Tapes: 0.5-2.0%; mouldings: 0.5-2.5% | Food crates: 0.5-1.5%; tapes: 1-3%; black tapes: 1-3% |
Sign Up for Our Newsletter!
[contact-form-7 id=”2272″ title=”Sign Up to Our Newsletter!”]