Overall Introduction of Polymer Antioxidant
What Is Antioxidant? (Definition of Antioxidant)
An antioxidant is a chemical compound that prevents oxygen from reacting with other compounds that are susceptible to oxidation. Polymer antioxidant, is a class of heat stabilizers, can be added to improve the shelf life of the product or to improve its high-temperature stability. While adding a stability margin during thermal processing.
Polymer Antioxidant Classification
Industry Antioxidant Types
| Type | features | Application |
| hindered phenolic | Excellent Hydrolysis resistance Extraction resistance Yellowing resistance Provide long-term stability | PE/PP pipe High crystalline PP Elastomer Nylon |
| Phosphites/Phosphonites | Excellent processing stability and color stability Heat stability, no residual impurity Hard precipitation, no adhere to water, No blooming, improve transparency of article Provide processing stability | PP/PE, elastomer, transparent article, PC, PC/ABS, nylon, POM etc. |
| thiosynergists | Long heat resistance better than DSTDP/ DLTDP No odor | For PP/PE need long-term stabilizing, filler modified PP/PE, wire, and cable |
| Metal Deactivators | Low melting point, easy to use Good stability, strong anti-aging Extraction stability Deactivate metal ion activity to prevent it boosting polyolefins degradation | PP/PE wire and cable Filled modified materials |
| Antioxidant blends | Excellent processing and color stability Heat stability, no residual impurity Granules form, no dust | Polyolefins, PC and PC alloy Nylon, styrenics, elastomer, POM |
Classified by Mechanism
Antioxidants can be divided into two classes, according to their mechanism in interrupting the degradation process: (a) chain-terminating primary anti-oxidants, and (b) hydroperoxide-decomposing secondary antioxidants
Primary Antioxidant react rapidly and are termed “radical scavengers'”.The most important are sterically hindered phenolics and secondary aromatic amines. Hindered phenolics are high molecular weight anti-oxidants for polymer systems that are sensitive to thermal and oxidative degradation, due to the formation of free radicals and peroxides. They protect against degradation at high processing temperatures and are highly efficient, low in volatility, and non-staining, with wide toxicological clearance and are effective at very low dosages (0.01-0.1%).
Secondary Antioxidant reacts with hydroperoxides to produce non-radical products and is therefore often termed ‘hydroperoxide decomposers’. They differ from primary phenols and amines in that they are decomposed by reaction with a hydroperoxide, rather than containing it. They are particularly useful in synergistic combinations with primary anti-oxidants. Phosphite/phosphonites are generally regarded as the secondary antioxidant.
Antioxidant Binary Blends, primary antioxidants plus a high-temperature hydrolytically stable organo-phosphite secondary antioxidant or thioesters plus phenolic antioxidant, Their use is limited to applications where possible effects on odor or taste and negative interaction with HALS (hindered amine light stabilizers) are not important.
Classification by Chemistry
Industrial Antioxidant additives also classified into phenolics, metal deactivates, amines, phosphites, thioesters and binary blends among the industry.
Classification by Application
Industrial Antioxidant can apply in plastics, synthetic fibers, elastomers, adhesives, tackifier resins, and waxes.
How Does Polymer Stabilizer (Antioxidant | UVA | HALS) Work?
Mechanism of polymer stabilizer as the photo below, polymer stabilizer include heat stabilizer and UV absorber / HALS (hindered amine light stabilizer). Heat stabilizer can subdivided into phenolics, amines, phosphites, thioesters, metal deactivates in this photo.
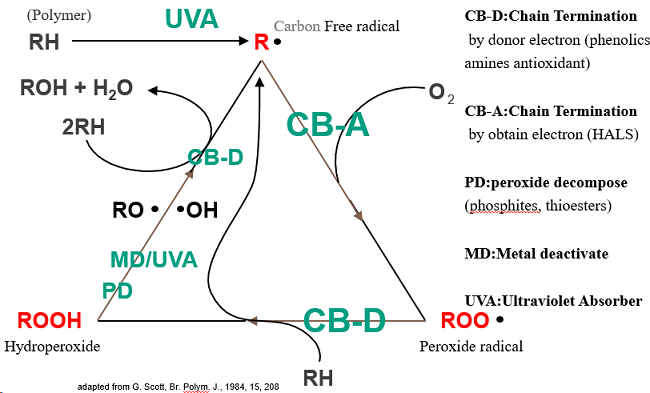
How to Choose Polymer Antioxidant?
General Rules to Follow When Choosing Antioxidant and UV Stabilizers
1. Stability & Extraction
Uv Stabilizers and antioxidant hydrolysis resistance are ok,it are the color stability needs to pay attention. Also, there two additives shall not react with other ingredients in a system, neither corrosion equipment nor extract by the substance on the article surface.
Hindered amine light stabilizer normally shows low alkalinity, no acidic additives shall be used together, and final article shall not apply in an acidic environment.
2. Solubility & Compatibility
Most polymers are non-polar while antioxidant, UV stabilizer are somewhat polar. Solubility is an issue need to concern. Antioxidant and UV stabilizers shall dissolve while not decompose in polymers processing temperature which most UV stabilizer could meet this requirement.
3. Migration
When possible, high molecule weight and relatively high melting point antioxidants and UVA shall be selected, each dosage shall determine based on most stringent processing and end-user environment.
4. Processing
When antioxidant and UV stabilizer melting range quite differ from resins’. Bias current or stick to screwing could occur. When this gap exceeds 100 ℃, UV stabilizer and antioxidant shall add in masterbatch form then mix with resin to process.
5. Handling and Safety
Antioxidant and UV stabilizer shall none or low toxic. No or low dust. Not harmful to human during plastic process and lifetime. Not harmful to animal or plates. No pollution to air,earth and water.
For agriculture file, food packing, toys, disposable infusion set or direct food, drug, medical device, medical devices, human contact plastics. Only FDA or EU approval antioxidant and UV stabilizer follow maximum concentration is allowed.
General Selection of Antioxidants for Use With UV Absorber
Care is needed in selecting anti-oxidants for use in combination with effective light-stabilization systems. High molecular weight stabilizers provide high levels of heat stability at normal application temperature. To avoid color shifts (especially yellow discoloration), BHT-free resins should be used with HALS formulations. Sulphur-containing organic compounds used as the-synergists are known to reduce the light stability level conferred by HALS, and high levels should be avoided.
| PE food contact | PE greenhouse film | PP colored food contact | (General purpose | PP tapes, moldings | PP colored food contact | |
| Base resin | PH | PE | PP | PH | PP | PP |
| HMW-HALS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low molecular weight | Yes |
| Benzophenone | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| food contact | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Thermal stabilization | good | good | Very good | Very good | Good | Limited |
| Application and let-down | Heavy-duty sticks: 1.5- 2.5%: film: 1.25-1.75%, 2.5-3.5%(24m); mouldings: 1.5-3% | Heavy-duty sacks: 1.5- 2.5%: greenhouse film: 1.25-1.75%. 2.5- 3.5 (24m) | Tapes: 1-3%; fibre: 1-3%: mouldings: 0.5-2.5% | Shrink wrap: 0.75-1.5%; greenhouse film:1-1.5%; HDPE crates: 0.25-0.5%; mouldings: 0.5-2.0% | Tapes: 0.5-2.0%; mouldings: 0.5-2.5% | Food crates: 0.5-1.5%; tapes: 1-3%; black tapes: 1-3% |
Typical Use of Antioxidant, UV Absorber, Light Stabilizer For Plastics
The information below is not to be construed as a warranty or representation for which we assume legal responsibility, it would change without any statement, Users should undertake sufficient verification and testing to determine the suitability for their own particular purpose of any information or products referred to herein.if any questions when choosing these additives for your material,please contact our support team by (Click Here).
For Antioxidants (Click Here), jump to antioxidant product portfolio page.
For UV Absorber/Light Stabilizer (Click Here), jump to product portfolio page.
| Material | Application | Antioxidants | UV Absorber/HALS | Remark | |
| POLYOLEFIN
| PP thick section | 260-280℃ Outdoor table&chair | 1010+DSTDP | 622+326 | DSTDP=3*1010 |
| PP thin section Fiber & strip | 240-300℃ | PP fiber:1425
| Fiber: 770 without heat 622with heat Strip:791 | Low volatile Heat stability Extraction resistance Gas yellowing | |
| HDPE | 180-240℃ blowing, injection, extrusion | 1010+168 | 791 ,944 | Compatibility | |
| LDPE | Film, packing, cover,mulch, greenhouse cover | 1010 | 622+531 | <0.1% | |
| LLDPE | Film, blowing, injection | 1010+168 | 944/622+531 | / | |
| PEX | Wire cable | TMB 6 | / | / | |
| PB | Pipe | 1010+ DLTDP | Extraction resistance | ||
| STYRENICS | PS | Instrument&lamp shell | 1076 | UV P+770 | / |
| SAN | Kitchenware Electrical Automotive | 1076+168 | UV P+770 | / | |
| IPS | / | 245,1076 | UV P+770 | 0.1~0.25% | |
| HIPS | 245 | / | / | ||
| MBS | / | 1076+DLTDP | / | / | |
| ABS | Machinery industry / | 245+DLTDP | UV P+770 | High dosage Based on process technical | |
| SIS | Hotmelt adhensive pressure sensitive adhesion | 1076/1010 0.1-0.5% | UV P+770 Hotmelt adhensive 213 /770 pressure sensitive adhesion 213/770 | ||
| SBS | Sole,tar regulator | 1076/1010 0.1-0.5% | UV P | ||
| POLYURETHANE | PUR | Form,RIM,coating, adhensive,fiber
| 1076+5057 Aromatic amines<0.05%
| leather,elastomer,textile, sole,adhensive, fiber need uv absorber, | Color stain mechanical property gas yellowing |
| ENGINEERING | PC | Window | 1076+168 | UV P,1577 | Color stain issue |
| POM | 220-230 | 245,1010 | 622+234 | Carbon black | |
| PET | Film,coating,bottle, Electricals,pipeline, conveyance | 1010 | 1577 | / | |
| PBT | 245 | 1577 | / | ||
| UPR | / | / | 329 | user to test and decide | |
| Aliphatic PA | Engine blade Heat sink cover etc. | 245/1098+168 | 944,770 | 0.2-0.7% | |
| TPEE | / | 329 | / | ||
| TPU | / | 1010/245+ DLTDP+445 | / | / | |
| PMMA | Glazing,signboard lamps | 0.05-0.2% UV P+770 Not always use together | / | ||
| PPE | / | / | UV P or 770 | ||
| PSU | / | / | / | exceed certain amount | |
| PVC | RPVC | / | / | UV P or 320 | |
| PPVC | / | 531+944 | |||
| ELASTOMER& | BR | 1520 | 320 | ||
| IR | 565 | 320 | |||
| SBR | Tire process, | 1520+TNPP | 320 | ||
| NBR | 1520+TNPP | ||||
| EPR,EPDM | Wire,roof film Liner,automotive | 1010 | 329+770 | ||
| Thermoplastic rubber | |||||
| TPO | 3052+168 | ||||
| X-SBR | Paper coating, carpet backing Nonwoven &textile liner | Cas 31851-03-3 Cas 26780-96-1 |
Market Trend of Polymer Antioxidant
In recent years, the development is mainly focused on the technical improvement of products, easier to handle and disperse.The main technical goal is a more lasting effect, at a lower dose level, to maintain good color and transparency when needed.The improved toxicological nature for food contact and medical applications is also a continuing goal for developers.In order to improve treatment, particles and liquid systems have been introduced and there is a general trend to greater use of masterbatch.
- Easier to handle/disperse
- Low dose level
- Durable effect
- Food Contact/Medical Application
- Particle/liquid