Overall Introduction of UV Absorber
What Is UV Absorber? Definition of UV absorber
These additives preferentially absorb the incident UV radiation and so protect the polymer from the radiation. UV absorbers do not themselves degrade rapidly, but they convert UV energy into harmless levels of heat energy, which are dissipated throughout the polymer matrix. UV absorbers are limited in their effectiveness because of the physical limitations of the absorption process, and their ability to absorb is governed by the need for high concentrations of additive and thickness of polymer before sufficient absorption will occur to retard the photodegradation effectively.
However, high concentrations of additive would be uneconomic and technically limited, while many applications (such as polyolefins) are in very thin sections, such as film and fiber. Benzophenones are good general-purpose UV absorbers for clear polyolefin systems, and can also be used in pigmented compounds. Benzotriazoles are used mainly in polystyrene. Both can also be used in polyesters. Concentrations are usually about 0.25-1.0%
Synonyms of UV absorber
- UV absorber agent
- UV stabilizer
- UV stabilizer agent
- ultraviolet absorber agent
- ultraviolet light absorber agent
UV Absorber Classification
The main function of UV absorbers is to absorb UV radiation in the presence of a chromophore (Ch) found in the polymer, the aim is to filter out the UV light that is harmful to the polymer before Ch* has had a chance of forming. Above all, a UV absorber must function within the 290 and 350 nm range. The purpose of UV absorbers is to absorb harmful UV light and quickly transform it into harmless heat. During this process, the absorbed energy is converted into vibrational and rotational energy of the molecule constituents. For UV absorbers to be effective, it is essential that this process takes place more rapidly than the corresponding reaction within the substrate, and that neither the UV absorber nor the polymer it is intended to stabilize is damaged during energy conversion. The most important UV absorbers are:
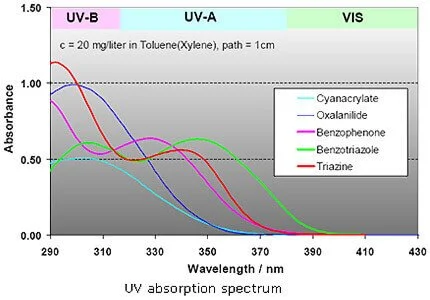
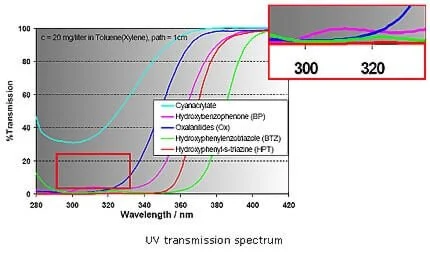
How Does UV absorber Work? mechanism of UV absorber
The main function of UV absorbers is to absorb UV radiation in the presence of a chromophore (Ch) found in the polymer, the aim is to filter out the UV light that is harmful to the polymer before chromophore free radical Ch* has had a chance of forming. Above all, a UV absorber must function within the 290 and 350 nm range. The effectiveness of UV absorbers is determined not only by their absorption characteristics but also, above all, by the Lambert-Beer Law.

Synergistic Effect Of Light Stabilizers And UV Absorber
UV absorbers are not able to absorb all of the UV radiation that a coating is exposed to. Some UV radiation will penetrate the coating surface. Because of this, HALS are incorporated into the polymers. These molecules work by scavenging any free radicals that do form – this is different from UV absorbers, which prevent their formation in the first place HALS function by removing radicals from the system and subsequently regenerating themselves. Most formulators will use a combination of absorbers and HALS for this reason.
Synergistic combinations of UV absorbers and HALS are optimal for the stabilization of polymer. UV absorbers are governed by the Beer-Lambert Law, thus absorbance is linearly related to the concentration of UVA (320 to 400 nanometers (used for photocuring), its molar absorptivity (extinction coefficient), and path length (coating thickness). HALS are free radical scavengers and are not subject to Beer’s Law and work anywhere in the coating system. HALS are especially effective at coating surfaces, providing better gloss retention, higher chalking resistance in pigmented systems while avoiding crack formation in clear coats. For pigmented systems, HALS provide the primary mechanism of stabilization, because most UV radiation is blocked by pigment from penetrating beyond the first few microns of a coating. The selection of the appropriate UVA/HALS combinations and concentration is dependent on the chemistry of polymer application system, the presence of pigments and fillers, film thickness and exposure conditions.
UV Absorber & Light Stabilizers Market And Trend
In the year 2015, global plastic and coating UV absorber (include light stabilizers) market scale is about 13 Billion RMB, and with 3% to 4% compound average growth rate(CAGR) in next four years. This attributes to industrial development in emerging market plus significant growth in demand for coating globally. For example, automotive and industrial paint has driven the demand for polymer additives. With the threshold of high techniques in additives manufacturing and developing, UV absorbers (include light stabilizers) manufacturers were located in few chemistry-developed countries. Opportunities for growth exist in the new market and exploring new applications.
How To Choose UV Absorber For Plastics?
General Rules to Follow When Choosing Antioxidant and UV Stabilizers
1. Stability & Extraction
Uv Stabilizers and antioxidant hydrolysis resistance are ok,it are the color stability needs to pay attention. Also, there two additives shall not react with other ingredients in the system, neither corrosion equipment nor extract by the substance on the article surface.
Hindered amine light stabilizer normally shows low alkalinity, no acidic additives shall be used together, and final article shall not apply in an acidic environment.
2. Solubility & Compatibility
Most polymers are non-polar while antioxidant, UV stabilizer are somewhat polar. Solubility is an issue need to concern. Antioxidant and UV stabilizers shall dissolve while not decompose in polymers processing temperature which most UV stabilizer could meet this requirement.
3. Migration
When possible, high molecule weight and relatively high melting point antioxidants and UVA shall be selected, each dosage shall determine based on most stringent processing and end-user environment.
4. Processing
When antioxidant and UV stabilizer melting range quite differ from resins’. Bias current or stick to screwing could occur. When this gap exceeds 100 ℃, UV stabilizer and antioxidant shall add in masterbatch form then mix with resin to process.
5. Handling and Safety
Antioxidant and UV stabilizer shall non or low toxic. No or low dust. Not harmful to human during plastic process and lifetime. Not harmful to animal or plates. No pollution to air,earth and water.
For agriculture file, food packing, toys, disposable infusion set or direct food, drug, medical device, medical devices, human contact plastics. Only FDA or EU approval antioxidant and UV stabilizer follow maximum concentration is allowed.
Selection of UV absorber and light stabilizers for plastics
here are list typical use of antioxidant, UV absorber, light stabilizer for each material, the information below is not to be construed as a warranty or representation for which we assume legal responsibility,Users should undertake sufficient verification and testing to determine the suitability for their own particular purpose of any information or products referred to herein.if any questions when choosing these additives for your material,please contact our support team by (Click Here).
For Antioxidants (Click Here), jump to antioxidant product page
For UV Absorber/Light Stabilizer (Click Here), jump to antioxidant product page.
| Material | Application | Antioxidants | UV Absorber/HALS | Remark | |
| POLYOLEFIN
| PP thick section | 260-280℃ Outdoor table&chair | 1010+DSTDP | 622+326 | DSTDP=3*1010 |
| PP thin section Fiber & strip | 240-300℃ | PP fiber:1425
| Fiber: 770 without heat 622with heat Strip:791 | Low volatile Heat stability Extraction resistance Gas yellowing | |
| HDPE | 180-240℃ blowing, injection, extrusion | 1010+168 | 791 ,944 | Compatibility | |
| LDPE | Film, packing, cover, mulch, greenhouse cover | 1010 | 622+531 | <0.1% | |
| LLDPE | Film, blowing, injection | 1010+168 | 944/622+531 | / | |
| PEX | Wire cable | TMB 6 | / | / | |
| PB | Pipe | 1010+ DLTDP | Extraction resistance | ||
| STYRENICS | PS | Instrument&lamp shell | 1076 | UV P+770 | / |
| SAN | Kitchenware Electrical Automotive | 1076+168 | UV P+770 | / | |
| IPS | / | 245,1076 | UV P+770 | 0.1~0.25% | |
| HIPS | 245 | / | / | ||
| MBS | / | 1076+DLTDP | / | / | |
| ABS | Machinery industry / | 245+DLTDP | UV P+770 | High dosage Based on process technical | |
| SIS | Hotmelt adhensive pressure sensitive adhesion | 1076/1010 0.1-0.5% | UV P+770 Hotmelt adhensive 213 /770 pressure sensitive adhesion 213/770 | ||
| SBS | Sole,tar regulator | 1076/1010 0.1-0.5% | UV P | ||
| POLYURETHANE | PUR | Form,RIM,coating, adhensive,fiber
| 1076+5057 Aromatic amines<0.05%
| leather,elastomer,textile, sole,adhensive, fiber need uv absorber, | Color stain mechanical property gas yellowing |
| ENGINEERING | PC | Window | 1076+168 | UV P,1577 | Color stain issue |
| POM | 220-230 | 245,1010 | 622+234 | Carbon black | |
| PET | Film,coating,bottle, Electricals,pipeline, conveyance | 1010 | 1577 | / | |
| PBT | 245 | 1577 | / | ||
| UPR | / | / | 329 | user to test and decide | |
| Aliphatic PA | Engine blade Heat sink cover etc. | 245/1098+168 | 944,770 | 0.2-0.7% | |
| TPEE | / | 329 | / | ||
| TPU | / | 1010/245+ DLTDP+445 | / | / | |
| PMMA | Glazing,signboard lamps | 0.05-0.2% UV P+770 Not always use together | / | ||
| PPE | / | / | UV P or 770 | ||
| PSU | / | / | / | exceed certain amount | |
| PVC | RPVC | / | / | UV P or 320 | |
| PPVC | / | 531+944 | |||
| ELASTOMER& | BR | 1520 | 320 | ||
| IR | 565 | 320 | |||
| SBR | Tire process, | 1520+TNPP | 320 | ||
| NBR | 1520+TNPP | ||||
| EPR,EPDM | Wire,roof film Liner,automotive | 1010 | 329+770 | ||
| Thermoplastic rubber | |||||
| TPO | 3052+168 | ||||
| X-SBR | Paper coating, carpet backing Nonwoven &textile liner | Cas 31851-03-3 Cas 26780-96-1 |
Selection Of Antioxidants For Use With UV Stabilizers
Care is needed in selecting anti-oxidants for use in combination with effective light-stabilization systems. High molecular weight stabilizers provide high levels of heat stability at normal application temperature. To avoid color shifts (especially yellow discoloration), BHT-free resins should be used with HALS formulations. Sulphur-containing organic compounds used as thio-synergists are known to reduce the light stability level conferred by HALS, and high levels should be avoided.
| PE food contact | PE greenhouse film | PP colored food contact | (General purpose | PP tapes, moldings | PP colored food contact | |
| Base resin | PH | PE | PP | PH | PP | PP |
| HMW-HAI.S | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Low molecular weight | Yes |
| Benzophenone | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| food contact | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Thermal stabilization | good | good | Very good | Very good | Good | Limited |
| Application and let-down | Heavy-duty sticks: 1.5- 2.5%: film: 1.25-1.75%, 2.5-3.5%(24m); mouldings: 1.5-3% | Heavy-duty sacks: 1.5- 2.5%: greenhouse film: 1.25-1.75%. 2.5- 3.5 (24m) | Tapes: 1-3%; fibre: 1-3%: mouldings: 0.5-2.5% | Shrink wrap: 0.75-1.5%; greenhouse film:1-1.5%; HDPE crates: 0.25-0.5%; mouldings: 0.5-2.0% | Tapes: 0.5-2.0%; mouldings: 0.5-2.5% | Food crates: 0.5-1.5%; tapes: 1-3%; black tapes: 1-3% |
Sign Up for Our Newsletter!
[contact-form-7 id=”2272″ title=”Sign Up to Our Newsletter!”]