Overall Introduction of Fluorescent Brightener
What Is Fluorescent Brightener?
Optical brightener sometimes called optical brightening agents (OBAs), fluorescent brightening agents (FBAs) or fluorescent whitening agents (FWA) are colorless to weakly colored organic compounds. When present on a substrate, absorb primarily invisible ultraviolet light in the 300-400 nanometer (nm) range and re-emit in the visible violet-to-blue fluorescent light to yield a brighter, fresher appearance. They are designed to brighten colors or mask yellowing in plastics, lacquers, paints, inks, photo-processing solutions and fibers.
Fluorescent Brightener Synonyms
Here we listed the synonym names of optical brightener which we often see and all refers to optical brighteners in most cases
FBAs
Optical Brightener Classification
1)Classification by Application
- Fluorescent brightener for detergent
include optical brightener CBS-X, DMS/AMS, CBS-155
- Fluorescent brightener for paper
include Optical brightener PC, BBU/ BBU-L, VBL/VBL-L
- Fluorescent brightener for fiber and textile
include optical brightener 4BK, ER-I/ER-I L, ER-II/ER-II L, EBF/EBF-L, PF / DT, BA, CXT, R4, MST-L, BAC, SWN / AW-L, WGS, NFW
- Fluorescent brightener for plastic
include optical brightener OB, OBR, OB-1, KSN, KCB, KSB, FP-127, CBS-127, PF
- Fluorescent brightener for paint and ink
include optical brightener UVT-1, ST, OEF, RT
2) Classification by Chemical Structure.
1. Toluylene type, with blue fluorescent light, used in cotton fiber, synthesis fiber, paper, soap industries.
2. Vanilla type, with coumarone structure and strong blue fluorescent light, use in celluloid, PVC plastics.
3. Pyrazoline type, with green fluorescent light, used in wool, polyamide, acrylic fibers.
4. Benzo nitrogen type, with red fluorescent light, used in acrylic fiber, PVC, PS.
5. Phthalimide type, with blue fluorescent light, used in terylene, acrylic fiber, cotton fiber.
3) Plastic Fluorescent Brightener Classification
1. Bisbenzoxazole, the chemical structure as below, OB, OB-1, KSN, KCB all belong to this chemical structure
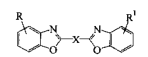
2. Phenyl coumarin, chemical structure as below
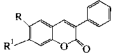
3. distyry-biphenyls, chemical structure as below, CBS-X is with this chemical structure
How Does Optical Brightener Work?
Optical brighteners or fluorescent whitening agents (FWA) are colorless to weakly colored organic compounds that, in solution or applied to a substrate, absorb ultraviolet light and re-emit most of the absorbed energy as blue fluorescent light between 400 and 500 nm.
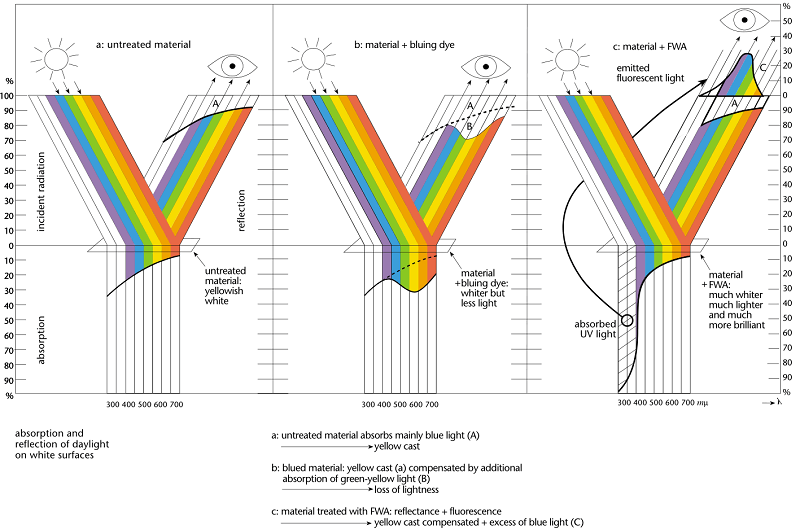 Materials that evenly reflect most of the light at all wavelengths striking their surface appear white to the human eye. Natural fibers, for example, generally absorb more light in the blue region of the visible spectrum (‘blue defect’) than in others because of impurities (natural pigments) they contain. As a result, natural fibers take on an unwanted, yellowish cast. Synthetic fibers also have this yellowish cast, although not as pronounced.
Materials that evenly reflect most of the light at all wavelengths striking their surface appear white to the human eye. Natural fibers, for example, generally absorb more light in the blue region of the visible spectrum (‘blue defect’) than in others because of impurities (natural pigments) they contain. As a result, natural fibers take on an unwanted, yellowish cast. Synthetic fibers also have this yellowish cast, although not as pronounced.
Whiteness in substrates can be improved by (1) increasing reflection (reflectance) or (2) compensating the blue defect. Bleaching has both of these effects to some extent, but invariably leave behind part of the yellowish cast. Even the most thorough bleach cannot remove all traces of a yellowish cast. Before the advent of fluorescent whitening agents (FWA), the common practice was to apply small amounts of blue or violet dyes (called ‘bluing’) to boost the visual impression of whiteness. These dyes absorb light in the green-yellow region of the spectrum, thereby reducing lightness. But, since at the same time they shift the shade of the yellowish material towards blue, the human eye perceives an increase of whiteness.
Unlike dyes, FWAs offset the yellowish cast and at the same time improve lightness because their bluing effect is not based on subtracting yellow-green light, but rather on adding blue light. FWAs are virtually colorless compounds which, when present on a substrate, absorb primarily invisible ultraviolet light in the 300-400 nanometer (nm) range and re-emit in the visible violet-to-blue fluorescent light. This ability of FWAs to absorb invisible short wavelength radiation and re-emit in the visible blue light which imparts a brilliant whiteness to the light reflected by a substrate is the key to FWAs effectiveness.
Test Of Optical Brightener
How To Choose Optical Brightener Agent?
General Guide
- Detergent optical brightener including CBS-X,DMS/AMS, CBS-155.
- Paper optical brightener includes PC, BBU / BBU-L, VBL/VBL-L.
- Fiber / Textile optical brightener contains 4BK, ER-I/ER-I L, ER-II/ER-II L, EBF/EBF-L, PF / DT, BA, CXT, R4, MST-L, BAC, SWN / AW-L, WGS, NFW.
- Plastic optical brightener includes OB, OBR, OB-1, KSN, KCB, KSB, FP-127, CBS-127, PF.
- Paint / Ink optical brightener are UVT-1, ST, OEF, RT.
Things to Know When Choosing Brightener Agent For Plastics?
Typical Optical Brighteners For Plastics, Detergent
Application | OBAs Adding Form | Typical OBAs | Issue to mind |
R-PVC | Dry powder mix | OB | Solubility Immigration resistance |
F-PVC | Dissolve or disperse in Plasticizer | OB | |
Transparent PVC | Plasticizer+OBAs Masterbatch OBAs+PVC Masterbatch | ||
PS | Dry powder mix before processing | OB | |
ABS | Dry powder mix before processing | OB | |
PC <300 | Dry powder mix before processing | OB | Heat stability; volatility |
PC >300 | Dry powder mix before processing | OB-1 | |
PU Film | Dry powder mix before process with granules or solution | Single component KCB | Immigration resistance Solubility |
PU Coating | Dry powder mix before process with a solution | / | |
PU Adhesive | Liquid or dispersion | / | |
PU form | Liquid | Polyhydric alcohol soluble | |
Polyolefin | Dry powder mix | KP 127 KSN | Compatibility PP>hdpe>ldpe Immigration resistance |
PMMA | Dry powder mix | OB KCB | Solubility |
UPR | Dissolve FWA into UPR Before curing | OB | Solubility No side effect during curing |
PET | polycondensation | OB-1 | After treatment necessary |
PA | Spinning | OB-1 | / |
Detergent Water base coating | Liquid | CBS-X | / |